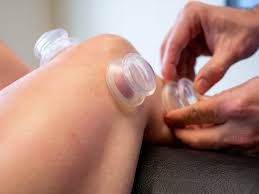
Myofascial cupping is a soft tissue therapy that encourages the release of tissue adhesions by oiling a large area of the body, creating a negative pressure or suction on the skin using silicone “cups,” and then moving or pulling the cups back and forth while the suction is in effect. This method is often used for myofacial release, lymphatic draining, for muscular pain, or to improve blood circulation. Other types of cupping include wet cupping and dry cupping.
Cupping – A therapy in Chinese medicine used after acupuncture and before gua sha or massage in which (traditionally, heated glass cups (also known as Fire Cupping) are applied to the skin along the meridians of the body for 5-15 minutes, creating suction as a way of stimulating the flow of energy (Qi). Modern cupping also utilizes plastic cups, bamboo cups and silicone cups. Types of cupping include fire cupping, wet cupping, dry cupping, needle cupping, and myofascial cupping.
Cupping Functions:
Moves Blood & Qi and breaks up obstructions
Detoxifies
Relieves Acute or Chronic Pain
Expels External Pathogens
Releases fascia, helps lymphatic drainage, and improves circulation.
Indications
Cupping therapy can ease (and often remedy) many conditions including: Headaches, muscle tension and stiffness, arthritis, sports injuries, fibromyalgia, and dysmenorrhea. Common cold, asthma, bronchitis, and allergies. Insomnia, stress and long standing emotional trauma.
Precautions:
Cupping is NOT recommended on areas of sensitive skin, ulcerated or broken skin, on the lumbar and abdominal region of pregnant women, or on people with excess hair (especially moving/myofascial/fire cupping). Cupping therapy often results in bruises (which will generally dissipate within 3 to 10 days). Fatigue and aching are common temporary side effects.
